| .github | ||
| .vscode | ||
| docs | ||
| include | ||
| lib | ||
| src | ||
| test | ||
| webapp | ||
| webapp_dist | ||
| .DS_Store | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| auto_firmware_version.py | ||
| COPYING | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| partitions_custom.csv | ||
| platformio.ini | ||
| README.md | ||
OpenDTU_VeDirect
Background
This project was started from this discussion (Mikrocontroller.net). It was the goal to replace the original Hoymiles DTU (Telemetry Gateway) with their cloud access. With a lot of reverse engineering the Hoymiles protocol was decrypted and analyzed.
I extended the original OpenDTU software to support also Victron's Ve.Direct protocol on the same chip. Additional information about Ve.direct can be downloaded from https://www.victronenergy.com/support-and-downloads/technical-information.
REST-API (/api/verdirectlivedata/status):
{
"data_age":0,
"age_critical":false,
"PID":"SmartSolar MPPT 100|30",
"SER":"XXX",
"FW":"159",
"LOAD":"ON",
"CS":"Bulk",
"ERR":"No error",
"OR":"Not off",
"MPPT":"MPP Tracker active",
"HSDS":{"v":46,"u":"Days"},
"V":{"v":26.36,"u":"V"},
"I":{"v":3.4,"u":"A"},
"VPV":{"v":37.13,"u":"V"},
"PPV":{"v":93,"u":"W"},
"H19":{"v":83.16,"u":"kWh"},
"H20":{"v":1.39,"u":"kWh"},
"H21":{"v":719,"u":"W"},
"H22":{"v":1.43,"u":"kWh"},
"H23":{"v":737,"u":"W"}
}
MQTT:
Sends text raw data as difined in VE.Direct spec.
Currently supported Inverters
- Hoymiles HM-300
- Hoymiles HM-350
- Hoymiles HM-400
- Hoymiles HM-600
- Hoymiles HM-700
- Hoymiles HM-800
- Hoymiles HM-1000
- Hoymiles HM-1200
- Hoymiles HM-1500
- TSUN TSOL-M800 (Maybe depending on firmware on the inverter)
Features for end users
- Read live data from inverter
- Show inverters internal event log
- Show inverter information like firmware version, firmware build date, hardware revision and hardware version
- Uses ESP32 microcontroller and NRF24L01+
- Multi-Inverter support
- MQTT support (with TLS)
- Home Assistant MQTT Auto Discovery support
- Nice and fancy WebApp with visualization of current data
- Firmware upgrade using the web UI
- Default source supports up to 10 inverters
- Time zone support
- Ve.Direct interface (via web-interface, REST-api, or MQTT)
Features for developers
-
The microcontroller part
- Build with Arduino PlatformIO Framework for the ESP32
- Uses ESPAsyncWebserver and Async MQTT client
-
The WebApp part
- Build with Vue.js
- Source is written in TypeScript
Wiring up
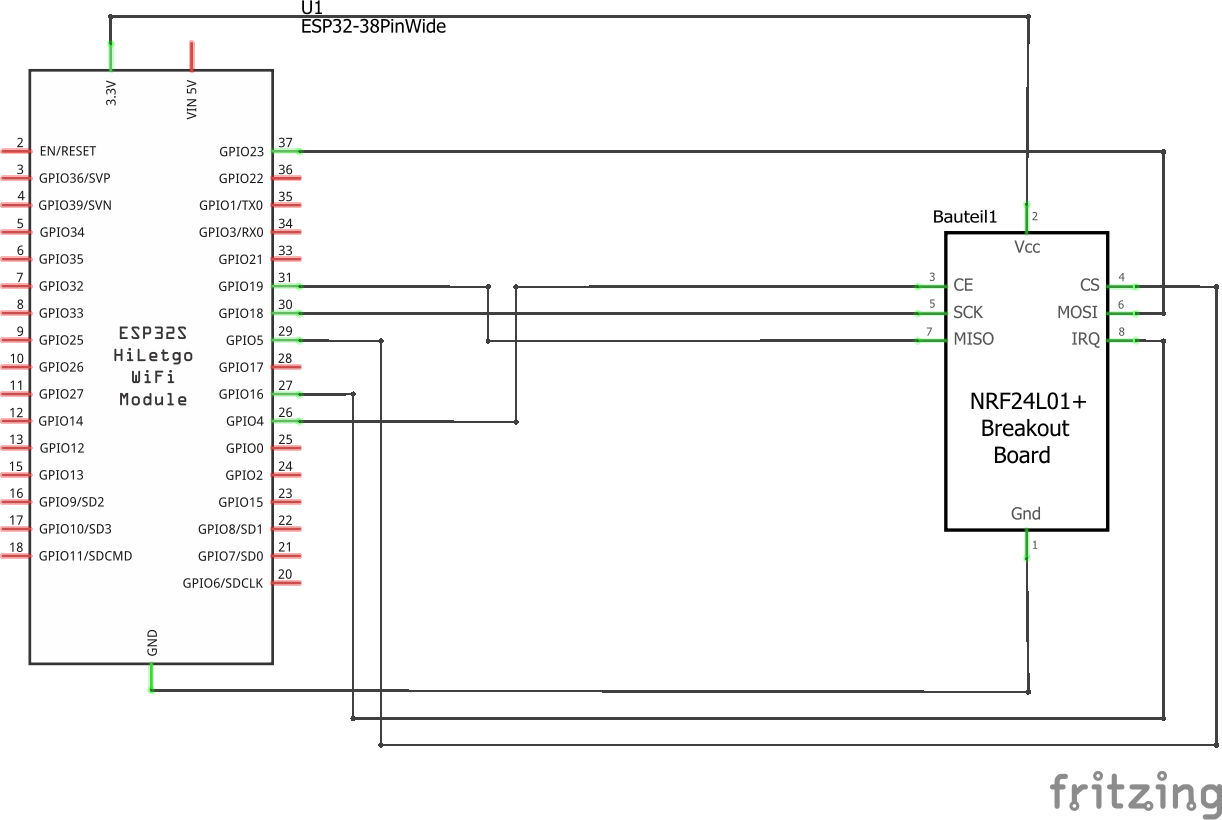
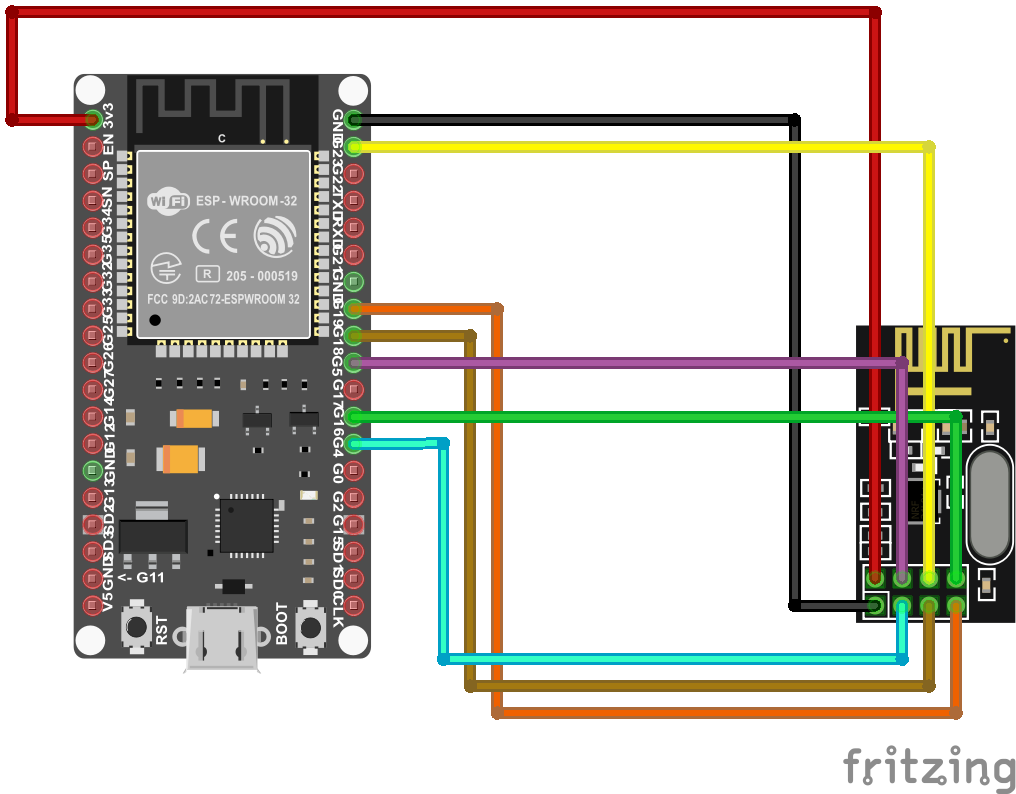
Schematic
Symbolic view
Change pin assignment
Its possible to change all the pins of the NRF24L01+ module. This can be achieved by editing the 'platformio.ini' file and add/change one or more of the following lines to the 'build_flags' parameter:
-DHOYMILES_PIN_MISO=19
-DHOYMILES_PIN_MOSI=23
-DHOYMILES_PIN_SCLK=18
-DHOYMILES_PIN_IRQ=16
-DHOYMILES_PIN_CE=4
-DHOYMILES_PIN_CS=5
-DVICTRON_PIN_TX=21
-DVICTRON_PIN_RX=22
Flashing and starting up
with Visual Studio Code
- Install Visual Studio Code
- In Visual Studio Code, install the PlatformIO Extension
- Clone this repository (you really have to clone it, don't just download the ZIP file. During the build process the git hash gets embedded into the firmware. If you download the ZIP file a build error will occur)
- In Visual Studio Code, choose File --> Open Folder and select the previously downloaded source code. (You have to select the folder which contains the "platformio.ini" file)
- Adjust the COM port in the file "platformio.ini". It occurs twice:
- upload_port
- monitor_port
- Select the arrow button in the status bar (PlatformIO: Upload) to compile and upload the firmware. During the compilation, all required libraries are downloaded automatically.
on the commandline with PlatformIO Core
- Install PlatformIO Core
- Clone this repository (you really have to clone it, don't just download the ZIP file. During the build process the git hash gets embedded into the firmware. If you download the ZIP file a build error will occur)
- Adjust the COM port in the file "platformio.ini". It occurs twice:
- upload_port
- monitor_port
- build:
platformio run -e generic - upload to esp module:
platformio run -e generic -t upload - other options:
- clean the sources:
platformio run -e generic -t clean - erase flash:
platformio run -e generic -t erase
- clean the sources:
First configuration
- After the initial flashing of the microcontroller, an Access Point called "OpenDTU-*" is opened. The default password is "openDTU42".
- Use a web browser to open the address http://192.168.4.1
- Navigate to Settings --> Network Settings and enter your WiFi credentials
- OpenDTU then simultaneously connects to your WiFi AP with this credentials. Navigate to Info --> Network and look into section "Network Interface (Station)" for the IP address received via DHCP.
- When OpenDTU is connected to a configured WiFI AP, the "OpenDTU-*" Access Point is closed after 3 minutes.
- OpenDTU needs access to a working NTP server to get the current date & time. Both are sent to the inverter with each request. Default NTP server is pool.ntp.org. If your network has different requirements please change accordingly (Settings --> NTP Settings).
- Add your inverter in the inverter settings (Settings --> Inverter Settings)
Flashing an Update using "Over The Air" OTA Update
Once you have your OpenDTU running and connected to WLAN, you can do further updates through the web interface. Navigate to Settings --> Firmware upgrade and press the browse button. Select the firmware file from your local computer.
You'll find the firmware file (after a successfull build process) under .pio/build/generic/firmware.bin.
After the successful upload, the OpenDTU immediately restarts into the new firmware.
Available cases
Building
-
Building the WebApp
- The WebApp can be build using yarn
$ cd webapp $ yarn install $ yarn build- The updated output is placed in the 'webapp_dist' directory
- It is only necessary to build the webapp when you made changes to it
-
Building the microcontroller firmware
- Visual Studio Code with the PlatformIO Extension is required for building